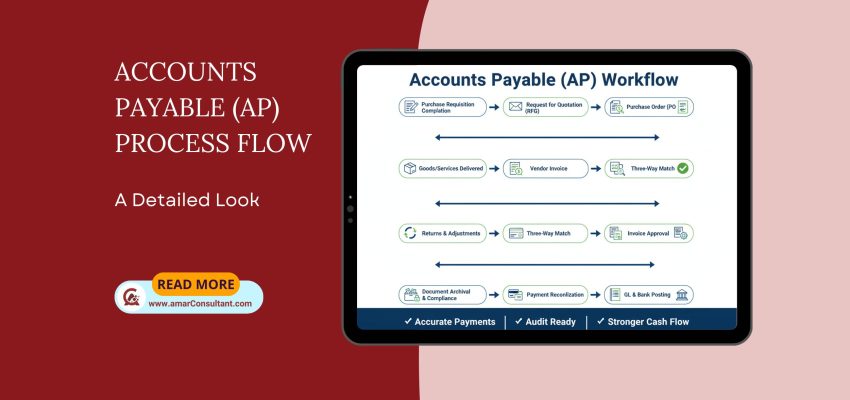
Streamlining the Accounts Payable (AP) Process Flow
💡 Have you ever wondered how a simple purchase request transforms into a paid invoice, navigating various checkpoints along the way? For every organization, the Accounts Payable (AP) process is the backbone of financial operations, ensuring timely payments, maintaining compliance, and fostering strong vendor relationships. Let’s embark on a detailed journey through the AP process,